*This website contains affiliate links. If you click on these and make a purchase, we will receive a small percentage of the sale.
You’ve heard of VPNs and proxies. Probably even used them until now. But are you aware of the differences between a proxy and a VPN – sort of like a proxy vs VPN showdown – and when you should use one or the other?
In this guide, you’ll learn what they are, their differences, and when to use them.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
- What is a proxy
- What is a VPN
- The Difference Between Proxy And VPN
- More differences between proxies and VPNs
- Proxy vs VPN: The major difference
- Which is better, a proxy or a VPN?
- Why use proxies if you have a VPN?
- When to use a proxy
- When to use a VPN
- How to use a proxy over VPN
- Troubles when using a proxy or VPN
- Why proxies are not suitable for privacy
What is a proxy?
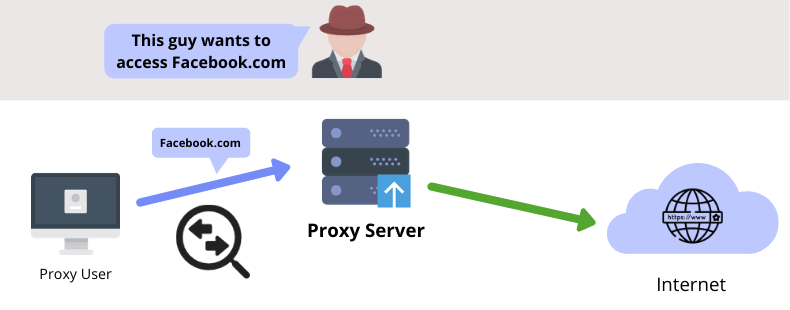
A proxy server acts as the intermediary between its users and the rest of the Internet.
In other words, a proxy server handles its users’ requests and forwards them to websites.
There are several types of proxies, such as: open and reverse proxies, HTTP/S proxies, SOCKS proxies and so on.
However, in this article, I will refer only to HTTP/S proxies. I am referring to them because these are the most commonly used proxies. And they represent more than 90% of the private proxy market.
At this stage, it’s not essential to make a difference between them. You need to know how they work and under what circumstances you might use them.
But, if you need a more detailed answer, you can check Wikipedia.
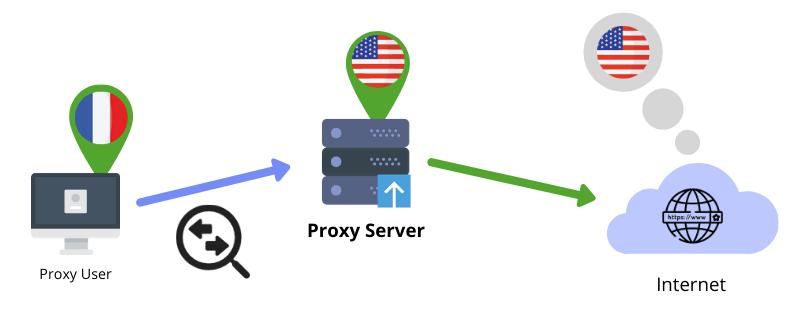
Here’s how proxies work:
- The user sends requests through the proxy server
- The proxy server recognizes the user’s request as valid and forwards them to the site’s web server
- The web server receives the request with the proxy server’s IP – which then recognizes as the user’s real location and IP address.
- The website returns the requested resources to the proxy server
- The proxy server receives the resources and forwards them to his user
PS: a couple of things to keep in mind: step (1) the user sends requests through the proxy server and step (3) the website recognizes the proxy server’s IP and location as being the user’s real one.
Keep these two things in mind as we move along.
Now, let’s see the other type of server, the VPN.
What is a VPN?
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a server that creates a secure connection to a remote network over the Internet.
When you connect to a VPN server, your device becomes part of that VPN’s network in the same way two computers connect in a local office (or home) network.
In other words, your device connects securely over the Internet to a remote network and becomes part of that network – in this way it also encrypts your traffic. And all your future requests will be forwarded through this network. Here’s more info on what is a VPN.
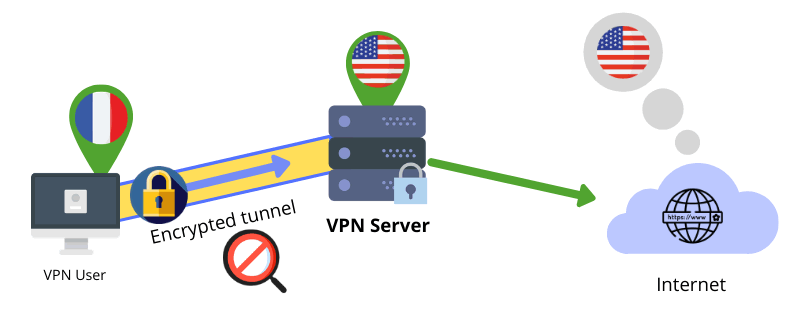
Here’s how a VPN works
- The user connects securely to the VPN server and the VPN server creates an encrypted channel between its network and the user’s device
- The user sends requests through the VPN server
- The VPN server forwards them to websites
- The website receives and sees the VPN’s IP and location as being the user’s real ones
- The site returns resources to the VPN, which in turn forwards them to its user.
Keep in mind: point (1) the user connects securely to the VPN server and point (4) the site recognizes the VPN’s details as being the user’s real ones.
The Difference Between Proxy And VPN
Now that you know how the two server types work let’s see the difference between a proxy and a VPN.
As I mentioned above, to keep in mind those two points from each server, you might have already spotted the difference.
Basically, point (3) from proxies and point (4) from VPNs are almost the same: they both connect their users to websites and display their [server] details as being their users’. So websites won’t know the real location and IP address of users connecting through proxies and VPNs.
From this point of view, a website can’t identify if you’re using a proxy or a VPN, because both of them hide your IP address. The web server can’t possibly know or make a difference.
Their similarities end here because they achieve this anonymity in different ways.
Here’s point (1) from proxies: the user sends his requests to the server.
And here’s point (1) from VPNs: the user connects securely to the VPN server.
This is a significant difference in how they work. A device connected to a proxy will start sending its requests without any prior connection.
While a device connecting to a VPN server first connects securely to the network and then tunnel its requests through it.
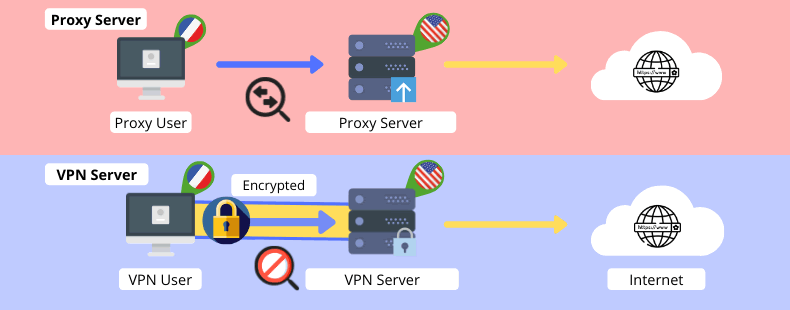
This is the main difference between the two.
You should use a VPN to hide your Internet traffic from your ISP and local government (by securing an encrypted channel).
ISP – Internet Service Provider – a company offering access to the Internet.
And you should use a proxy server to hide your real IP address and location only from the websites you want to access.
Is a proxy the same as a VPN? More differences between proxies and VPNs
No, they are not the same thing. As you saw above, they are different. They do their job of masking your IP address differently.
And each one comes with its advantages and drawbacks.
Proxy PRO:
Multiple connections – You can send several requests simultaneously through multiple proxy servers
Proxy CON:
Lack of privacy – Your ISP and local government can see your web-requests
VPN PRO:
Privacy and anonymity – Your ISP can’t see your traffic and browsing history
VPN CON:
Single connection – once you connect to a VPN server, you can’t connect, at the same time, to another VPN server
The major difference between the two
They connect and do their job differently. But the main difference between proxy and VPNs is the level at which connections take place.
A proxy connects you at an app-level (you connect your browser, or a script through proxies).
A VPN connects your whole device (hence, at a device level) and forwards all your web requests through the VPN (including your browser, Skype client, Windows Updates, torrents, etc).
This is why people use VPNs for privacy and anonymity. When you connect to a VPN server, nobody located between your device and the VPN server will be able to sniff your traffic (here I am talking about your ISP and local government).
For example, with the increased scrutiny of Internet privacy and anonymity, the VPN market has exploded in recent years.
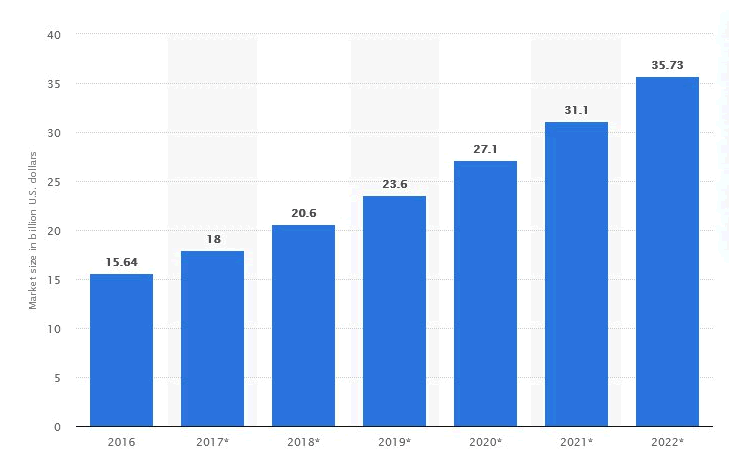
Size of VPN market worldwide
The VPN market growth can be better observed based on its users per country. Here you can see that VPN adoption is higher in countries with a high level of Internet censorship and information control.
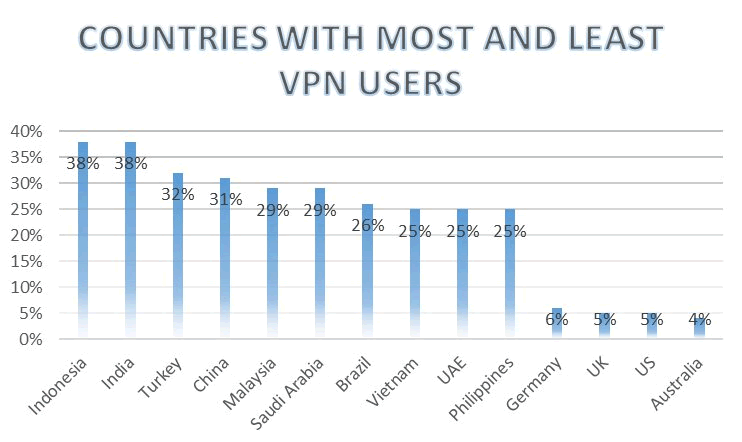
Meanwhile, the proxy market is not as large as the VPN one because its uses are more specialized – mainly marketers and developers use proxies. Whereas a VPN tends to be used by regular Internet users.
Which is better, a proxy or a VPN?
It’s a question asked by many people.
But the answer is not a straight-forward one because you can’t merely say that in a comparison proxy vs. VPN one is better than the other.
It all depends on how you plan to use them.
Why use proxies if you have a VPN?
Let’s clarify one thing: users do not use proxies for privacy and anonymity.
To better illustrate their differences and the need to use either one or the other, here are a few common use-cases for bot proxies and VPNs.
When to use a proxy
Proxies are mainly used for tasks where you need to change your IP address often, or you need multiple IP addresses at the same time.
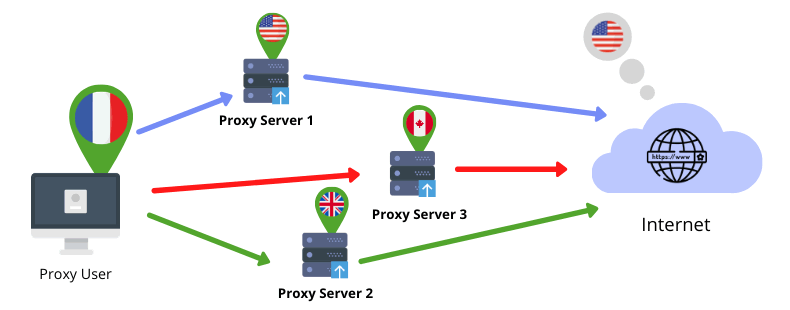
One great feature of proxies is its distributed access. You can share your proxy login details with several other people.
For example, you can allow remote workers or clients to access a web resource through the proxy server IP. The website you want to access will see all your requests (from you and other people) originating from the same location. In this way, you avoid any unnecessary blocks set in place when an account is accessed from a remote corner of the world.
Common proxy servers use cases:
1) Avoid account blocks – by always using the same proxy IP address, even when traveling, you don’t risk having your account blocked.
2) Account protection – assign a proxy IP to an online account. Marketers managing multiple social media accounts on behalf of their clients, assign an IP address for each account. They do so to isolate each account and avoid having multiple accounts blocked if one of their clients’ accounts is locked for any particular reason.
NOTE: most social networks identify accounts based on the IP address they use; that’s why, if you manage multiple accounts, it’s best to use a different IP address for each of them.
3) Automation – developers and software engineers use proxies for automation. They use proxies to send multiple web requests at once or to distribute their requests over a wider geographical area.
4) Data mining – from web scraping to crawling content, data mining is one of the most requests-intensive tasks of a project. Proxies are used to distribute requests through multiple IP addresses and to avoid an account block.
5) Ad verification – proxies are used to connect to search engines to retrieve ads information either manually or automatically. For example, a marketer living in New York can’t test what ads Google displays in California, because his IP address is from NYC. So, all results returned by Google are for the NYC area. Whereas if the marketer uses multiple California proxies (e.g., Los Angeles, San Diego, San Francisco) at the same time and accesses Google Search, the results and ads displayed by the search engine will be those for the geographical location where the proxy server is located.
6) Pentesting – ethical hackers and information security specialists can use proxies to test a website without getting blocked or to avoid rate-limiting.
What criteria and features to look for when buying proxies?
With more than 70 private proxy providers, when looking to buy proxies check the following:
1) High-anonymity (elite) proxies – these are proxies that won’t disclose the fact that they are proxy servers
2) Multiple server locations – this is an indication the provider is serious and offers a good enough service to maintain such a network
3) Money-back guarantee – this is always a thing you should look for, just in case their service is not satisfactory and you need to get a refund.
When to use a VPN
While proxies have more specialized use, VPNs are consumer-oriented, which means people use them for personal purposes.
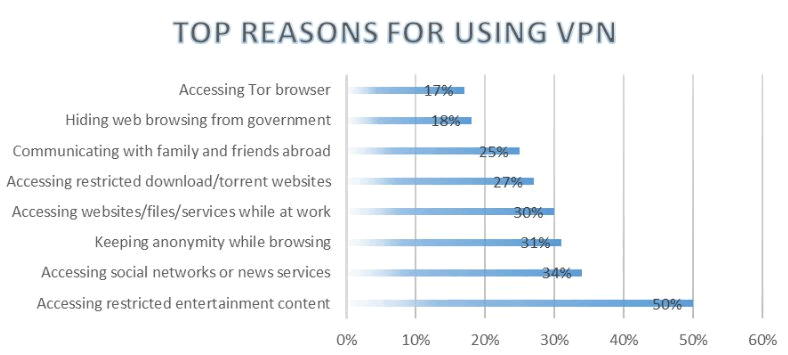
As you can see, their usage usually boils down to:
1) Anonymity – to avoid getting blocked by local governments and ISPs.
2) Privacy – to communicate safely and securely without fearing interferences from third parties.
What criteria and features to look for when buying a VPN?
The VPN market is much more crowded than the proxy market. Currently, there are more than 80 VPN providers, without taking into account VPN providers that offer only mobile apps via app stores.
So, when looking to buy a VPN, check the following:
1) The number of servers – VPN servers are usually more crowded then proxies, so you’ll need to get a provider with a large number of servers
2) Privacy and No Logs Statement – VPNs are used for privacy, so you need to make sure the provider won’t log your traffic.
3) Money-back guarantee – it’s always an excellent option to have in case their service is not satisfactory
Can you use a proxy and a VPN at the same time? How to use a proxy over VPN
You might not be aware, but this is a commonly used setup by marketers and developers from countries with restricted Internet.
Here’s how it works:
1) They connect to the VPN server to gain access to the open Internet
2) The VPN connection is established at the device level
3) They set a proxy in their browser or script to forward requests from their device (via the VPN) to the proxy server, which then sends it to websites
4) Any accessed website in this way sees the proxy server’s IP as the user’s one (Not the user’s real one neither the VPN’s one)
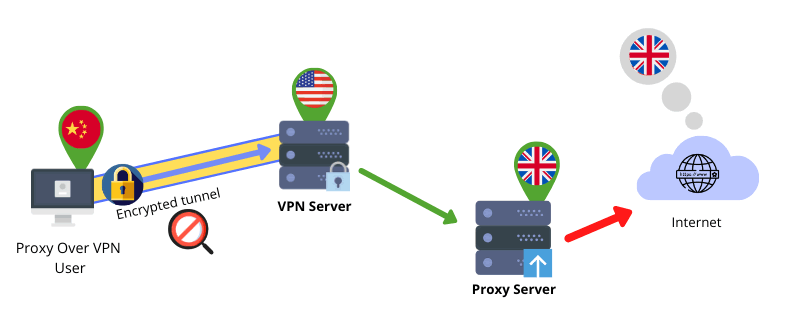
The bottom line is that you can use a proxy over a VPN. However, you can’t do it the other way around. Because a VPN needs a direct connection to establish the encrypted tunnel between your device and the VPN servers.
Can I get in trouble using a proxy or VPN?
Yes, you can get in trouble depending on where you are located.
For example, VPN usage is either restricted or blocked in several countries such as China, Turkey, Russia, or Iran.
As a matter of fact, in China, according to ZDNet, one guy was arrested for distributing a VPN illegally.
It is not the usage per se that gets you in trouble, but what you plan on doing with proxies and VPNs. If you want to do illegalities, then yes, you can get in trouble using either one of them.
ProtonVPN has more info on what countries restrict VPN usage and to what extent.
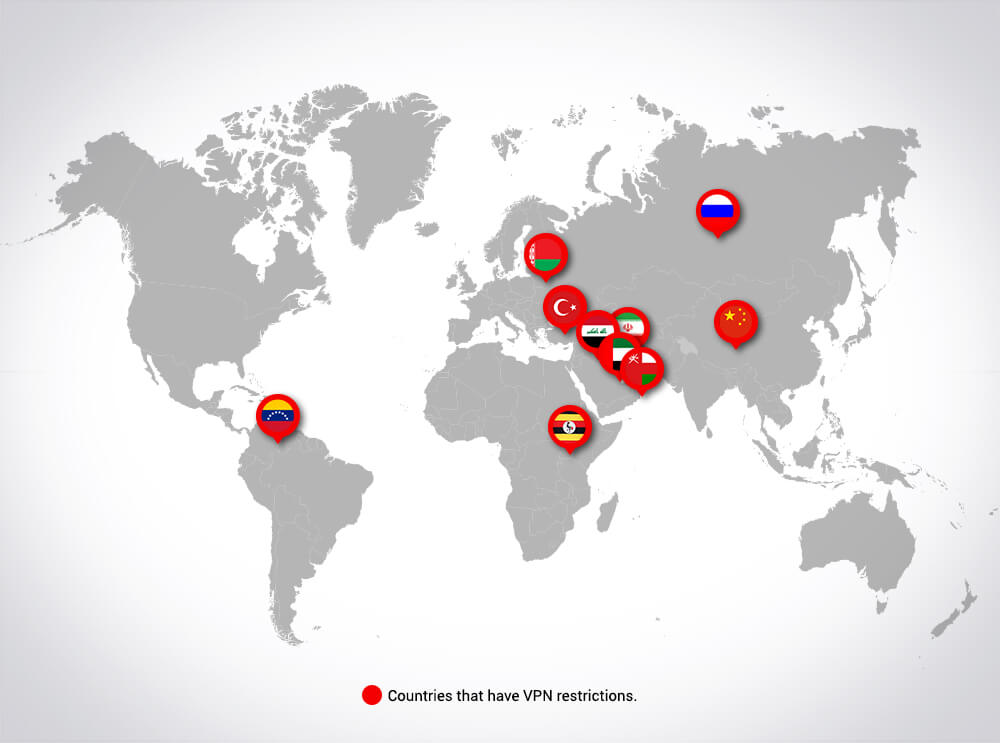
Countries where VPN usage is restricted
How ‘private’ are https proxies? Why proxies are not suitable for privacy
I think I should dedicate a whole section to this question because it’s an important one. And knowing the answer to it can help you stay on the safe side of things.
Let me start.
A proxy server is not suitable for privacy and anonymity for one single reason: it can’t create an encrypted channel between your device and the proxy server. And always, the DNS request to access a website is sent in plain text.
DNS request: the request your device sends to find the IP address of the webserver of a site. A DNS request for Facebook.com will return 31.13.65.36, which your PC uses then to connect to Facebook.com
Why is DNS sent in plain text?
A DNS server acts as a phone book matching domain names with IP addresses.
On a proxy connection, the DNS request is always sent in plain text because the proxy server doesn’t have an SSL certificate (to establish an HTTPS connection – S stands for secure). It will handle SSL connections only after the target website initiates an SSL connection with the user.
So, when you use a proxy server and type Facebook.com in the browser, the DNS request is sent to the proxy server in plain text.
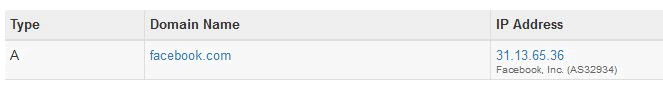
Moreover, all your communication will be transmitted in plain text until the Facebook.com web server establishes an SSL connection with your device and returns its resources through the proxy. Only at this point, your connection becomes private.
The same plain-text connection type happens when you don’t use a proxy server and you use your ISP’s DNS server.
Basically, on a regular connection, over HTTP, there is a complete lack of privacy until the website you want to access establishes the HTTPS connection via SSL.
However, this shouldn’t be a concern for you unless your ISP (or local government) blocks your access to specific websites. In which case, you need a VPN to establish an encrypted connection before your DNS request gets sent in plain text.
To sum it up
There is a difference between proxy and VPNs. Both of them connect you to websites and mask your real IP address and locations. However, the way a proxy vs. VPN does it is that a proxy won’t encrypt your traffic, whereas a VPN will.
There’s no right or wrong tool. Both proxies and VPNs are useful. You only need to identify your needs and if your project needs either one or the other.
PS: Stay away from free stuff (free proxies and free VPNs). They’re free for a reason (they say that when something is free, the product is you, as in the case of social media). Usually, free proxies and free VPNs end up selling their users’ Internet data and traffic history to third parties – this is their monetization. Just think about why somebody would spend large amounts of money every month to maintain a server infrastructure and then offer access to it for free.








